- Home
- About Us
- Service
- Application
- Technology
- Resource
- Contact Us

LIUDUS®
HaploX has pioneered the development of cutting-edge bioinformatics software, machine-learning models, and data libraries. These tools form the backbone of our data processing infrastructure, enabling efficient sequencing data analysis, error removal, and precise detection of low-frequency mutations.
Bioinformatics Software
01
Fastp
HaploX's Fastp enhances data preprocessing by integrating features from commonly used tools for quality control, adapter trimming, and per-read quality pruning. Developed in C++ with multi-threading support, Fastp operates significantly faster, as validated in studies showing it to be two to five times quicker while maintaining or surpassing the quality of data filtering and mutation detection.
Published in Bioinformatics in September 2018, Fastp is available as an open-source tool on GitHub.
02
Gencore
HaploX’s Gencore efficiently removes redundant sequencing information and offers memory-efficient PCR duplicate removal and consensus read generation for NGS data, with or without UMIs. It provides informative statistical reports to aid quality control and downstream analysis. Published in BMC Bioinformatics in December 2019, Gencore is available as an open-source tool on GitHub.
03
MutScan
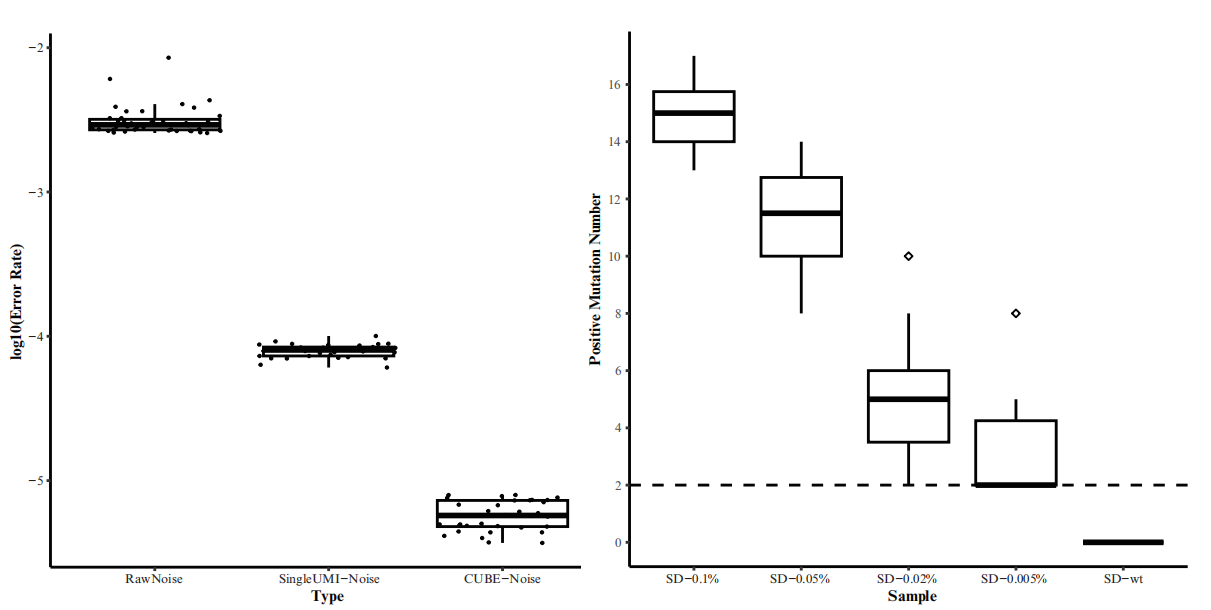
MutScan is a high-performance tool for detecting and visualizing target mutations, significantly improving detection sensitivity. Unlike traditional pipelines, MutScan can directly detect target mutations from raw FASTQ files using a high-error-tolerance string searching algorithm. It validates detected mutations and those identified by conventional pipelines through an HTML report, evaluating mutation confidence via multiple metrics.
Published in BMC Bioinformatics in January 2018, MutScan is available as an open-source tool on GitHub.
04
GeneFuse
Designed for clinical applications, GeneFuse offers fast, sensitive detection and visualization of target gene fusions. It bypasses the alignment step typical of most tools, scanning raw sequencing data directly, thereby achieving higher sensitivity and specificity.
Published in the International Journal of Biological Sciences in May 2018, GeneFuse is available as an open-source tool on GitHub.
05
FineMSI
FineMSI is HaploX's patented tool for analyzing microsatellite loci and determining MSI status using the earth movers' distance (EMD) method. It evaluates the dissimilarity between MSI-high and MSI-low data distributions, offering greater sensitivity and specificity than standard NGS-based MSI methods. FineMSI showcases its potential as a precise method for MSI status determination.
Machine Learning
HaploX leverages machine learning to tackle complex image denoising and target recognition challenges. By training workflows on extensive real-world data, we can minimize manual intervention, enhancing our ability to detect low-frequency cancer mutations and thereby improving the sensitivity and specificity of genetic tests.
01
MrBam
MrBam, HaploX's patented software, uses machine learning models trained on vast datasets of background noise and false-positive mutation sites to filter variant noise effectively.
02
TCRnodseek
TCRnodseek accurately classifies benign and malignant pulmonary nodules using a support vector machine that integrates TCR characteristics and clinical information. Based on a study of 99 individuals with indeterminate lung nodules, TCRnodseek demonstrated robust sensitivity (76%), specificity (91%), accuracy (84%), and an AUC of 0.8. The clinical results were published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy in October 2022.
Luo, H., Zu, R., Huang, Z. et al. Characteristics and significance of peripheral blood T-cell receptor repertoire features in patients with indeterminate lung nodules. Sig Transduct Target Ther 7, 348 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01169-7
Data Libraries

01
Data Libraries
HaploX's proprietary data libraries, built from extensive real-world sequencing data, facilitate mutation interpretation:
1. HapKnow: Annotates over 1.4 million tumor somatic mutations.
2. HapHeal: Annotates over 1.3 million hereditary mutations.
These libraries underpin our HapReport system, providing automated mutation reporting with concise clinical significance interpretations.
By integrating innovative bioinformatics tools, machine learning models, and comprehensive data libraries, HaploX continues to lead in genetic testing solutions, ensuring precise and efficient mutation detection and interpretation.