
- Home
- About Us
- Service
- Application
- Technology
- Resource
- Contact Us

Astral-DIA Proteomics
Product Overview
Quantitative proteomics precisely identifies and quantifies all proteins in a sample. Data-independent acquisition (DIA), a cutting-edge mass spectrometry technique, fragments all parent ions within a set mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) range, capturing comprehensive fragment information without omission. This boosts data utilization and protein identification numbers compared to traditional label-free methods, with superior accuracy and reproducibility over data-dependent acquisition (DDA), making it ideal for large-scale cohorts.
Leveraging the Thermo Orbitrap™ Astral™ platform—integrating quadrupole, Orbitrap, and revolutionary asymmetric track lossless Astral analyzer—HaploX delivers unprecedented speed, coverage depth, sensitivity, and quantitative accuracy. This groundbreaking instrument excels at trace-level protein detection, with no sample number limitations, enabling large-scale sample analysis.
Advantages
![]() Low Sample Requirements: Only 200 ng of peptides per sample is needed
Low Sample Requirements: Only 200 ng of peptides per sample is needed
![]() Superior identification depth and sensitivity: 50% more protein identifications vs. conventional methods; excels at low-abundance peptide detection.
Superior identification depth and sensitivity: 50% more protein identifications vs. conventional methods; excels at low-abundance peptide detection.
![]() Customizable workflows: Standard 8/24-minute detection + personalized solutions.
Customizable workflows: Standard 8/24-minute detection + personalized solutions.
![]() Full-process QC: Pre-treatment + MS quality control system with extensive sample type experience.
Full-process QC: Pre-treatment + MS quality control system with extensive sample type experience.
![]() High Throughput: Unlimited sample quantity, suitable for large-scale studies.
High Throughput: Unlimited sample quantity, suitable for large-scale studies.
![]() Stable Quantification: DIA technology ensures high coverage, reproducibility, and accuracy with reduced data acquisition randomness.
Stable Quantification: DIA technology ensures high coverage, reproducibility, and accuracy with reduced data acquisition randomness.
Product Parameters
| Indicator | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Instrument Platform | Thermo Orbitrap Astral |
| Turnaround Time | 30 Working Days |
| Delivery Standard | Raw Data + Standard Analysis |
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Samples | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|
| Human/Animal Tissue | Regular tissues (heart, liver, spleen, lungs, intestines, kidneys, etc.) | 15mg |
| Tough Tissue (Cartilage) | 200mg | |
| Plant Tissue | Soft Tissue (Leaves, Flowers of Woody Plants; Herbs, Ferns, Bryophytes) | 100mg |
| Tough Tissue (Tree Roots, Bark, Branches, Fruits, Seeds, etc.) | 2g | |
| Microorganisms | Common Bacteria, Fungal Species | 50mg |
| Cells | Suspension/Adherent Cultured Cells (Due to different cell sizes, the volume must meet the required standard) | 30uL, 5'10^6 Cells |
| Liquid Samples | Plasma/Serum | 50uL |
| Saliva/Bile | 500uL |
Workflow
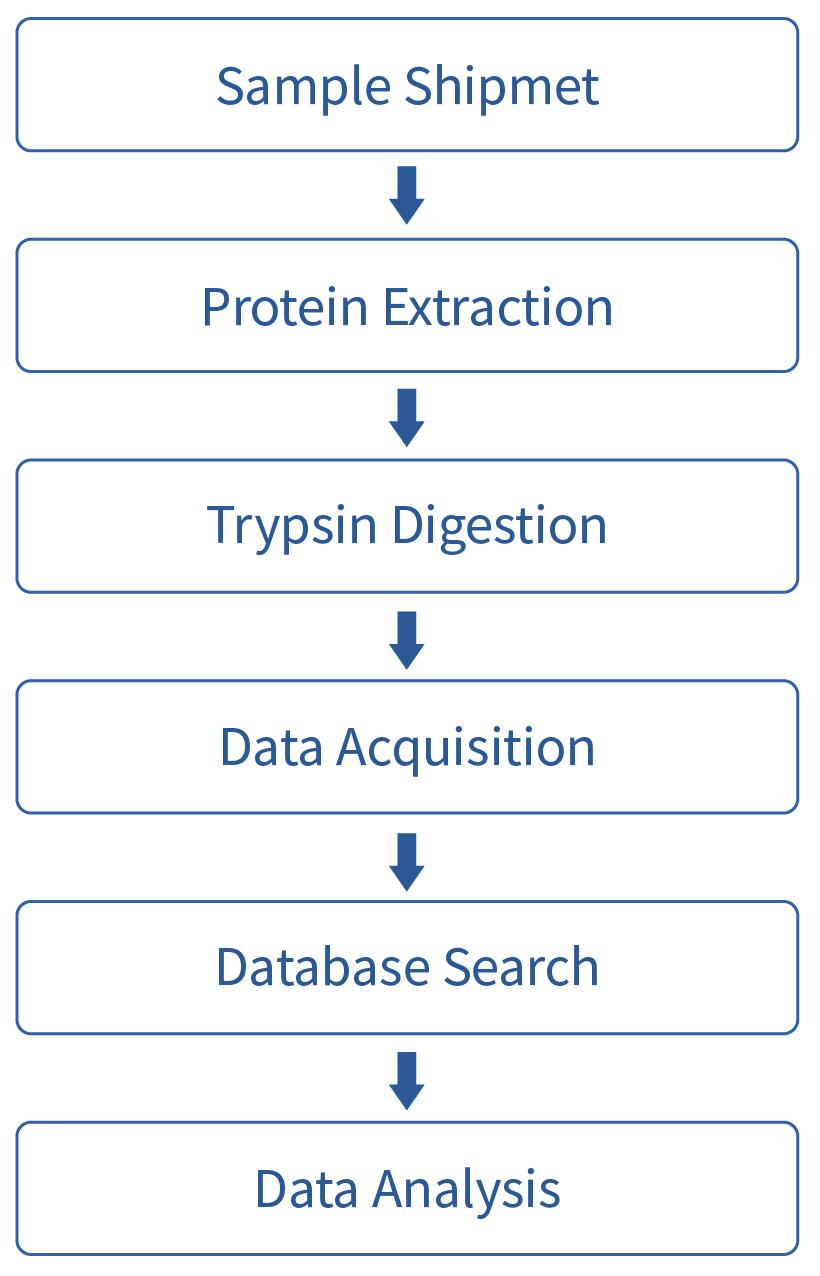
Analysis Contents
| Standard Data Analysis | |
|---|---|
| Quality Control | Peptide charge/length/FDR distribution, missed cleavage rate statistics. |
| Identification | Statistical results of identified proteins for individual samples and the overall dataset. |
| Functional Analysis | Pathway enrichment (GO, KEGG, Reactome, Wikipathways), chromosomal localization, subcellular localization. |
| Cells | Suspension/Adherent Cultured Cells (Due to different cell sizes, the volume must meet the required standard) |
| Differential Expression | Statistics of differentially expressed proteins, bar plots, volcano plots, cluster analysis, pathway enrichment of differentially expressed proteins. |
| Multi-group Comparison | Statistics of differentially expressed proteins and functional analysis |
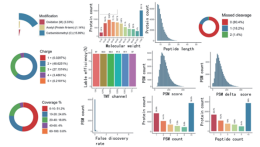


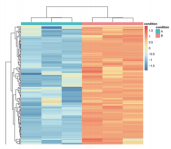
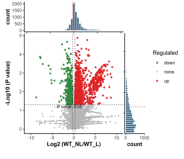
Protein Identification Numbers
| Sample Type | Time | Identification Range |
|---|---|---|
| Human Cells | 8min | 5492-10100 |
| 24min | 9513-11233 | |
| Human Tissues | 8min | 6050-9464 |
| 24min | 9589-12000 | |
| Mouse Tissues | 8min | 4795-8615 |
| 24min | 4688-12000 |
Application Scenarios
![]() Biomedical Research and Biomarker Discovery
Biomedical Research and Biomarker Discovery
![]() Drug Discovery and Development
Drug Discovery and Development
![]() Clinical Application
Clinical Application
![]() Agricultural Science
Agricultural Science
FAQ
Q:What is Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) in proteomics?
A: In proteomics, DIA is a mass spectrometry-based strategy that systematically fragments all precursor ions within predefined mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) windows. This approach enables unbiased data collection, high reproducibility, and high-throughput protein quantification when analyzing complex biological samples.
Q:What are the advantages of DIA-based quantitative proteomics over traditional label-free quantification?
A: Traditional label-free quantification generally requires fractionation, which is time-consuming, poorly reproducible, and yields results with low reliability. In contrast, DIA-based quantitative proteomics represents a next-generation label-free technology. Through an optimized data acquisition mode, it captures more comprehensive information within the same timeframe. This not only shortens the experimental cycle but also significantly improves the reproducibility of inter-sample comparisons, resulting in highly reliable data outcomes.
Q:How does Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) compare to Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA) in terms of quantification performance and reproducibility?
A: DIA outperforms DDA in consistency and data completeness by capturing fragment data from all ions during each analytical run. This characteristic minimizes missing values and enhances inter-sample reproducibility, making it particularly suitable for large-scale studies or longitudinal experiments where reliable cross-sample comparisons are critical.
